Using the new KiCad IPC API in a CI environment
22.03.2025KiCad 9 introduced a new IPC API. The old SWIG-based Python bindings are now deprecated and are planned for removal in the next major release. Plugin developers are encouraged to start migrating.
The old API has one major advantage over the new one from a testing and continuous integration
perspective - it works without running a GUI application and requires no extra setup for use in
Docker containers or CI agent machines.
Currently, the new API requires running instance of the PCB Editor. Although there are plans
to enable headless mode via kicad-cli, at the time of writing, the only way to use the new API is
by launching pcbnew (the GUI application) first.
Here’s an example of how to work around this limitation and use the IPC API in Python within Linux-based Docker containers:
Add
xvfbto the Docker image. This is a virtual display.Add the
PyVirtualDisplayPython package to your requirements. This wrapper simplifies usingxvfb.Write some code that uses the above tools to start the
pcbnewprocess. For example:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104import json import os import subprocess import time from pathlib import Path import kipy from pyvirtualdisplay.smartdisplay import DisplayTimeoutError, SmartDisplay class LinuxVirtualScreenManager: def __enter__(self): self.display = SmartDisplay(backend="xvfb", size=(1024, 768)) self.display.start() return self def __exit__(self, *exc): self.display.stop() return False def screenshot(self, path): try: img = self.display.waitgrab(timeout=5) img.save(path) return True except DisplayTimeoutError as err: print(err) return False def get_kicad_config_dir() -> Path: return Path.home() / ".config/kicad/9.0" def enable_ipc_api() -> None: settings_file = get_kicad_config_dir() / "kicad_common.json" if not settings_file.is_file(): settings_file.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True) # Most likely, pcbnew has never been executed, so create a minimal config with open(settings_file, "w") as f: print("Creating minimal settings file") min_settings = { "api": {"enable_server": True, "interpreter_path": ""}, } json.dump(min_settings, f, indent=2) else: with open(settings_file, "r") as f: settings = json.load(f) if not settings["api"].get("enable_server", False): print("Enabling IPC API") settings["api"]["enable_server"] = True with open(settings_file, "w") as f: json.dump(settings, f, indent=2) def prepare_mock_fp_lib_table() -> None: # Create a mock fp-lib-table file in the config directory if it doesn't already exist # This prevents a popup on the first pcbnew run fp_lib_table_path = get_kicad_config_dir() / "fp-lib-table" fp_lib_table_path.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True) if not Path(fp_lib_table_path).is_file(): with open(fp_lib_table_path, "w") as f: f.write("(fp_lib_table)") def wait_for_kicad(kicad, timeout: float, interval: float = 1.0): start_time = time.time() while time.time() - start_time < timeout: try: kicad.ping() return except (kipy.errors.ApiError, kipy.errors.ConnectionError): pass time.sleep(interval) raise TimeoutError(f"KiCad did not respond within {timeout} seconds.") if __name__ == "__main__": # Prepare minimal configuration files for running pcbnew enable_ipc_api() prepare_mock_fp_lib_table() # Run pcbnew inside a virtual display with LinuxVirtualScreenManager() as mgr: p = subprocess.Popen( ["pcbnew"], env=os.environ.copy(), # This is important, as it sets the DISPLAY variable ) try: kicad = kipy.KiCad() wait_for_kicad(kicad, 5, 0.2) version = kicad.get_version() print(f"KiCad version: {version}") except Exception as e: print("Failed to use IPC API") print(e) _ = mgr.screenshot("screenshot.png") p.kill()To verify this code, you can use the
admwscki/kicad-kbplacer-primary:9.0.0-jammyimage:1 2 3 4 5$ mkdir ipc-example && cd ipc-example # Create ipc_example.py and copy the example code above $ docker run --rm -v $(pwd):$(pwd) -w $(pwd) \ admwscki/kicad-kbplacer-primary:9.0.0-jammy /bin/bash -c \ "pip3 install kicad-python PyVirtualDisplay && python3 ipc_example.py"The container should run, install dependencies, and finish by printing version information like this:
KiCad version: 9.0.0-9.0.0-2~ubuntu22.04.1. It should also produce ascreenshot.pngfile in the current directory: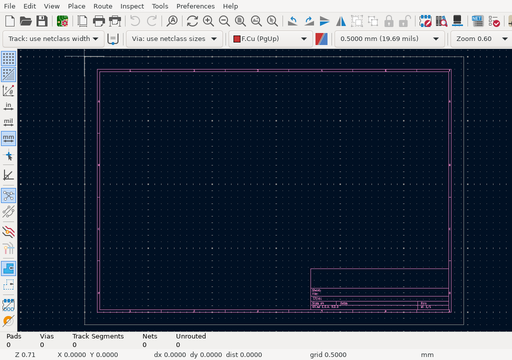
For a more complete example, including running on CircleCI’s Windows
agent and better pytest integration, check out the changes in the kbplacer repository 1.
On Windows, the general approach is the same, with two key differences:
- There is no virtual display and extra OpenGL drivers must be installed.
- Modifying KiCad’s configuration files before the first run must be extended to prevent extra popups, which apparently happen only on Windows.
As a result, the kbplacer plugin now has its first test using the new API, which appears in the pytest report like this:
Although having a headless KiCad mode would be ideal, using the new API in a Dockerized/CI environment is feasible.